Home
Episode 3 Supports
Episode Description
Exploring: Keoni and Sasha extend their use of the Pythagorean theorem. They determine the x-value for a point on the parabola that has a y-value of 5.
Students’ Conceptual Challenges
Representing an unknown distance on the grid can be challenging. Here the distance from the point on the parabola when y = 5 and the y-axis is unknown [1:32].
- Sasha and Keoni incorrectly label this distance as b2 [1:37] but correctly treat it as b, which is 4.5 [2:42]. This inconsistency is addressed later in Lesson 3, Episode 4.
- Sasha and Keoni incorrectly label this distance as b2 [1:37] but correctly treat it as b, which is 4.5 [2:42]. This inconsistency is addressed later in Lesson 3, Episode 4.
Focus Questions
For use in a classroom, pause the video and ask these questions:
1. [Pause video at 1:40]. How does Keoni know that the distance from the point on the parabola to the focus is 6?
2. [Pause video at 2:50]. Sasha wrote 4.5 above the b2. What does the 4.5 represent?
Supporting Dialogue
Ask your students to reflect on the usefulness of the Pythagorean theorem by asking:
- Why does the Pythagorean theorem work here?
- How do the lengths of the sides of the triangle help you find the coordinates of the point on the parabola?
- Why does the Pythagorean theorem work here?
Math Extensions
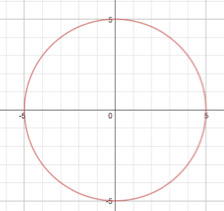
1. A circle is the set of points that are equal distance from a fixed point (called the center). The graph below is of a circle with the center at the origin. Can you find the x-value of a point on the circle below when the y-value is 4? Explain your reasoning.
2. Find the x-value of a point on the circle shown below when the y-value is 2. Explain your reasoning.
Mathematics in this Lesson
Lesson Description
Targeted Understanding
CC Math Standards
CC Math Practices
Lesson Description
Keoni and Sasha work with a parabola on the coordinate grid. They use the properties of the grid and the Pythagorean theorem to determine if the coordinates of a point are on a given parabola. They apply these methods to find the missing x-value of a point on the parabola for a given y-value.
Targeted Understandings
This lesson can help students:
- Identify and apply key elements of the geometric definition of a parabola in the context of the Cartesian coordinate grid.
- Conceive of a point on a Cartesian coordinate grid, not only as a location, but also as representing distances in 2-dimensional space.
- Apply the Pythagorean Theorem in a new setting to measure distance.
Common Core Math Standards
• CCSS.M.HSG.GPE.A.2: Derive the equation of a parabola given a focus and directrix.
Lesson 2 connects the geometric definition of a parabola from Lesson 1 with an algebraic coordinate grid, which makes the derivation of an equation of a parabola possible. Sasha and Keoni then derive the equation of:
o particular parabolas in Lessons 3 and 4;
o any parabola with vertex (0,0) in Lesson 5; and
o any parabola with vertex (h,k) in Lesson 9.
• CCSS.M.HSG.GPE.B.4. Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically.
Sasha and Keoni use the coordinates on an algebraic Cartesian grid, along with the definition of a parabola, to validate that three points are on the parabola.
• CCSS.M.8.G.B.8. Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points in a coordinate system. Keoni and Sasha use the Pythagorean theorem, along with the coordinate system and the definition of a parabola, to determine the x-value for a point on the parabola given its y-value.
Common Core Math Practices
CCSS.Math.Practice.MP5 Use appropriate tools strategically.
In this lesson, Sasha and Keoni use an important mathematical tool— the Pythagorean theorem. A discussion in the lesson models an important habit of mind related to tool use. Specifically, when Keoni and Sasha are stumped about how to measure the length of a diagonal line segment from a point on the parabola to the focus [1:46, Episode 2], their teacher encourages them to write down everything they know [1:56, Episode 2] and articulate what they are trying to find [2:53, Episode 2]. In the process, a right triangle emerges on the grid, with two sides of known length and one of unknown length. This practice of analyzing the situation prepares Sasha and Keoni to strategically apply the Pythagorean theorem once the teacher suggests its use [3:56, Episode 2].